ARTICLE SUMMARY
The performance evaluation process is essential to developing an action plan focused on employee development and growth.

What is performance evaluation?
Performance evaluation (also known as performance review or performance appraisal) refers to the process of systematically assessing an employee’s performance.
It is especially useful for understanding each employee’s individual abilities and limitations in order to calibrate training, determine compensation, and calculate suitability for advancement.
What are the benefits of a performance evaluation process?
In addition to identifying an employee’s strengths or weaknesses, performance evaluations provide additional benefits. For employers, this process informs strategic planning, protects against possible litigation, and boosts employee morale. For employees, the process improves communication, defines performance goals, and helps with individual and team development.
Definitive Guide to HR Workflow ManagementDownload now
Performance evaluation stats
The data tells us that feedback is valuable, and employees want to discuss work performance, goals, and career opportunities more frequently with their managers.
| Employees who had conversations with their manager in the last six months about their goals and successes were 2.8 times more likely to be engaged (Gallup) |
| 33.4% of employees would like more feedback from their managers (Joblist) |
| Employees who are involved in setting their goals at work are 3.6 times more likely to be engaged (Gallup) |
| Highly engaged business units saw a 28% reduction in shrinkage and 40% of reduction in quality defects (Gallup) |
| 94% of employees would stay at a company if it invested in their career (LinkedIn) |
| 45% of millennials, 31% of Gen Xers, and 18% of baby boomers agree that a job that accelerates their professional or career development is “very important” (Gallup) |
7 performance appraisal examples and types
There are many ways to evaluate employee performance, but here are seven common methods:
- Self-appraisal. Employees set aside time at specified points during the year to examine their progress towards goals, noting successes and failures along the way.
- Manager appraisal. During this 1:1 meeting, managers discuss an employee’s performance and suggest potential training opportunities. Managers should come equipped with information such as objective-based goals, employee self-appraisals, and peer reviews.
- 360-degree feedback. Besides manager and self-appraisal, employees who undergo 360-degree reviews are also rated by their peers and/or any external customers or partners they work with frequently.
- Objective-based feedback. An objective-based appraisal is based on mutually agreed-upon goals for a specific period. For example, did the employee meet or exceed production goals?
- Human resources accounting. HR weighs the cost of hiring, training, and nurturing an employee against the revenue they generate for the company.
- Skill assessment. The assessment center appraisal method consists of several standardized tests and exercises.
- Behaviorally anchored rating scale. BARS is a series of standardized data points that managers use to appraise their employees.
Keep in mind that performance evaluation methods aren’t one-size-fits-all. Depending on what you want to measure and how, you can create a custom plan using any of these ways either combined or on their own.
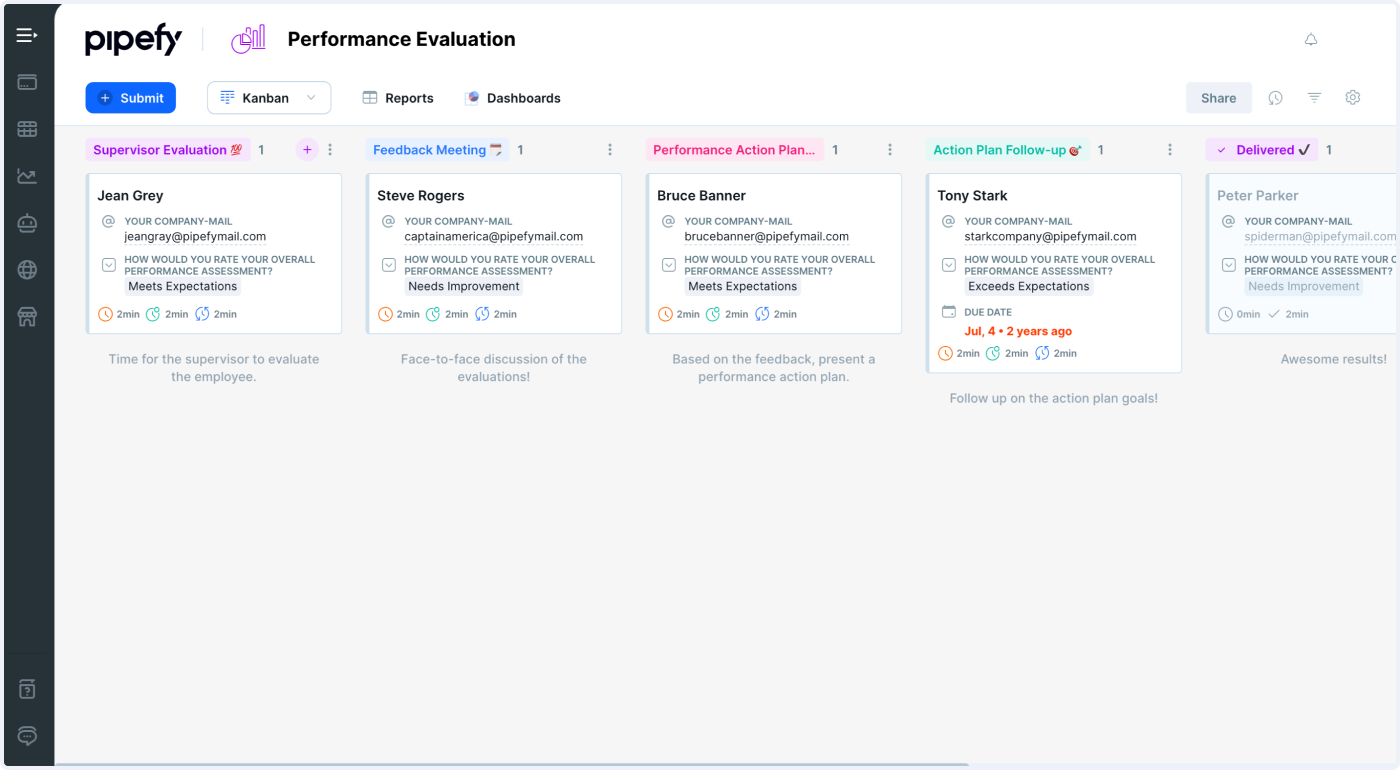
Build a scalable performance evaluation process
The performance evaluation process normally consists of:
- Employee evaluations. The employee evaluates their performance according to pre-established criteria.
- Manager evaluations. The manager evaluates the employee and their performance according to the aforementioned criteria.
- Feedback meetings. Manager and employee meet face to face to discuss the results of the evaluations, plus compare and contrast the gathered information.
- Action plans. Both parties work together towards developing an action plan to keep/improve the performance results.
- Follow-ups. Employees and managers schedule subsequent meetings to keep track of the goals established on the action plan.
Using the performance evaluation examples and types mentioned in the previous section, it’s time to start building an employee performance evaluation process.
Not sure what’s right for you? Consider this common performance evaluation process example of a performance evaluation: an objective-based evaluation that involves an employee self-appraisal, a manager review, and 360-degree feedback that includes peer reviews.
Process framework
Once you understand which elements of the employee performance evaluation you’d like to include, use these steps to build out your process:
- Establish the purpose of the evaluation process to better understand what you want to measure, why, and how. With a clear idea of the process in mind, performance evaluations can go from dreaded to empowering.
- Set goals, performance expectations, success criteria, and the timeline for giving feedback.
- Survey employee and team members.
- Review whether employees met their goals and performed according to the established expectations and criteria. Keep this step interactive and conversational, avoid turning it into a lecture.
- Evaluate the results and determine next steps.
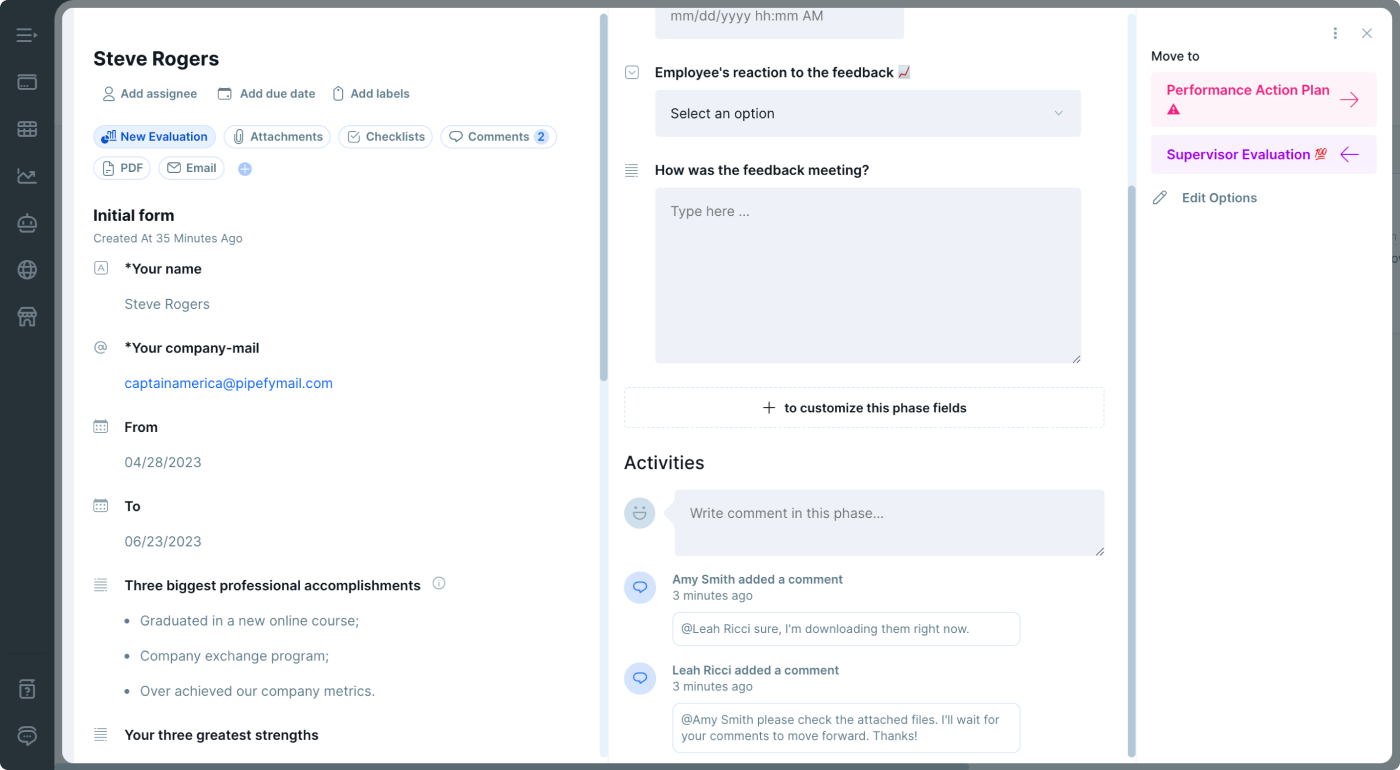
Process frequency
The performance evaluation process is the starting point for employees and managers to create a development plan. For the workforce of yesteryear, the performance evaluations were reserved for the annual review. However, that review frequency is falling out of favor with today’s workers, with many preferring ongoing feedback rather than one big meeting per year.
Investing in continued communication and frequent conversations are extremely helpful to keep everyone on the same page. Also, scenarios in which managers and employees have a strong relationship with frequent communication help make performance evaluations less stressful for both parties.
5 tips to improve performance evaluations
Use a no-code software tool to organize and manage your employee performance evaluation process.
With a performance management system, you can continuously align organizational objectives with employee competency, incentives, and development, in addition to reducing the stress of performance management and improving process consistency.Automate steps in your process.
With HR automation rules, you can automate repetitive tasks, such as sending notifications and emails to reviewers and updating employees automatically once their performance evaluation is complete.Standardize feedback collection.
Forms standardize the data collection process for consistency and reporting.Save time with process templates.
Using a customizable template is the fastest way to build the process.Follow the feedback-proof-suggestion model.
Rather than just calling out a problem or praising employees with no context, have a clear conversation that provides employees feedback, context for the feedback, and how they can either improve or build upon their current performance. This way employees can have a full picture of their current performance.If you’re ready to improve your performance evaluation process, read up on how the best employee management tool can motivate teams.
Invest in your team’s development with Pipefy
Pipefy is a no-code solution that makes it simple to design and build performance evaluation processes to build and launch scalable, automated workflows without writing a single line of code. And with customizable dashboards, you can translate raw data — like projects completed, deadlines hit or missed — into visual dashboards for a full picture of how your employees are performing.
Pipefy also offers a free performance evaluation template that allows you to set up feedback meetings with your employees as well as collect and give feedback, helping them improve their performance as well as overall behavior.
The adaptable template is fast and simple to deploy and can be customized for your unique needs. You can also connect your existing tools and processes with Pipefy to centralize employee data and build an end-to-end HR operation.